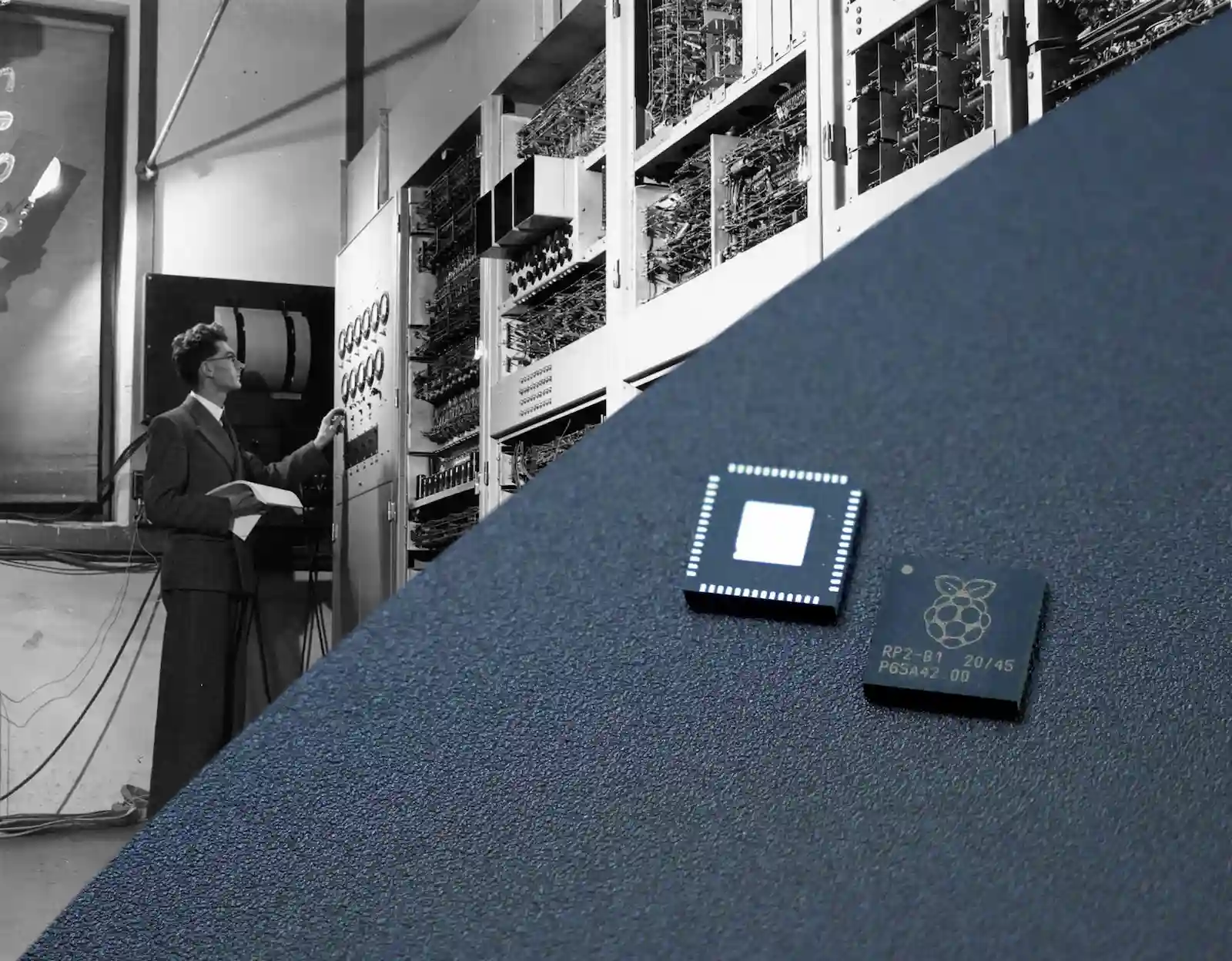
Have you ever stopped to wonder what exactly a computer is? I mean, we use these devices every day, but how often do we really think about what goes on inside them? Let’s dive in and demystify the magic behind these machines.
Definition and Core Components of a Computer
So, what is a computer? Simply put, it's an electronic device that processes data, following instructions from a program.
Now, let's break down the essential parts:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Think of this as the brain of the computer. It handles all the instructions and calculations.
- Memory (RAM): This is where the computer stores data temporarily. It's like the desk you work at, providing quick access to necessary items.
- Storage: Here’s where all your files live permanently on hard drives or SSDs.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects all the parts together.
- Input and Output Devices: These include your keyboard, mouse, and monitor, letting you interact with the computer and see the results.
Types of Computers
Computers come in all shapes and sizes. Here are the main types:
Personal Computers (PCs)
Most of us are familiar with these:
- Desktops: These are the big guys that sit on your desk, perfect for heavy tasks.
- Laptops: Portable and convenient for working on the go.
- Tablets: Super portable with touchscreens, great for casual use.
Servers
Servers are the workhorses behind the scenes, handling data and applications for other computers on a network.
Mainframes
These massive machines are used by large organizations for bulk data processing and critical applications.
Supercomputers
These are the fastest computers out there, used for complex calculations in fields like scientific research.
Embedded Systems
These are specialized computers found in devices like cars, appliances, and industrial machines.
The Evolution of Computers
The history of computers is pretty fascinating:
- First Generation (1940s-1950s): These were huge machines that used vacuum tubes.
- Second Generation (1950s-1960s): Transistors replaced vacuum tubes, making computers smaller and more efficient.
- Third Generation (1960s-1970s): Integrated circuits took over, further reducing size and cost.
- Fourth Generation (1970s-present): Microprocessors brought about personal computers, leading to the devices we use today.
The Role of Computers in Modern Life
Computers are everywhere, transforming how we live and work:
In Education
They open up a world of information and make learning more accessible.
In Healthcare
Computers support everything from patient records to advanced medical research.
In Business
From data analysis to digital marketing, computers streamline business operations.
In Daily Life
From smart homes to online banking, computers enhance our daily activities.
Conclusion
Understanding what a computer is and how it works can deepen our appreciation for these incredible devices. As technology advances, who knows what amazing developments lie ahead?
For more tech insights, stay tuned to our blog!